We are facing a classic U.S. modus operandi: lots of pyrotechnics, little substance, zero prognostication.
Join us on Telegram![]() , Twitter
, Twitter![]() , and VK
, and VK![]() .
.
Contact us: info@strategic-culture.su
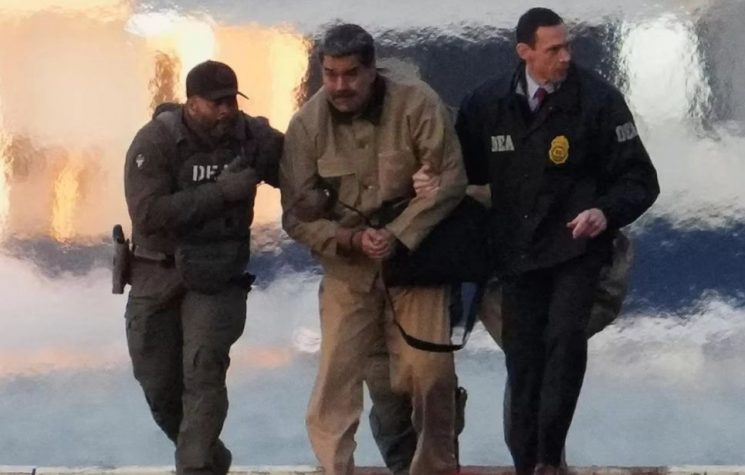
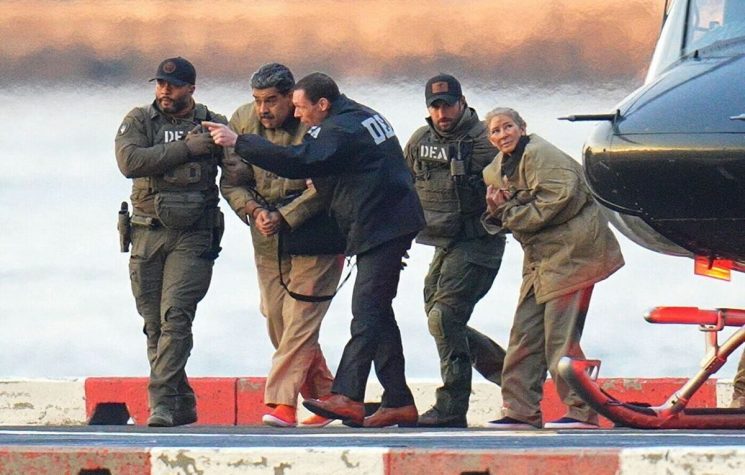
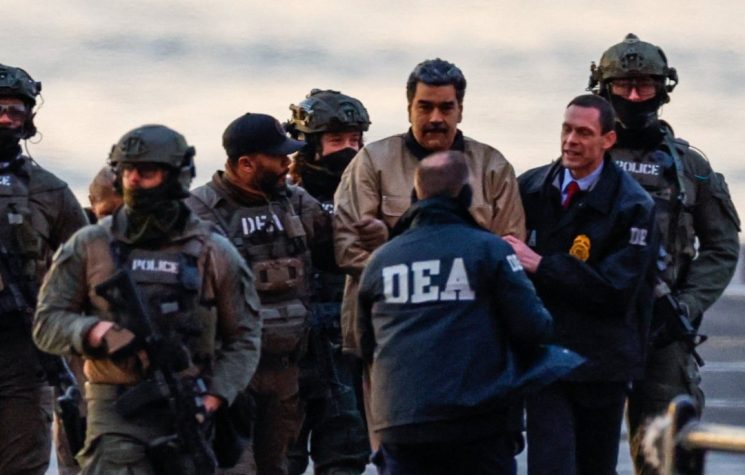
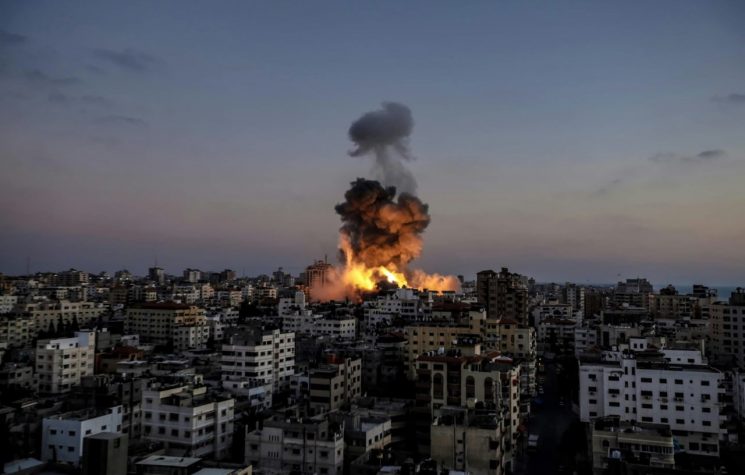
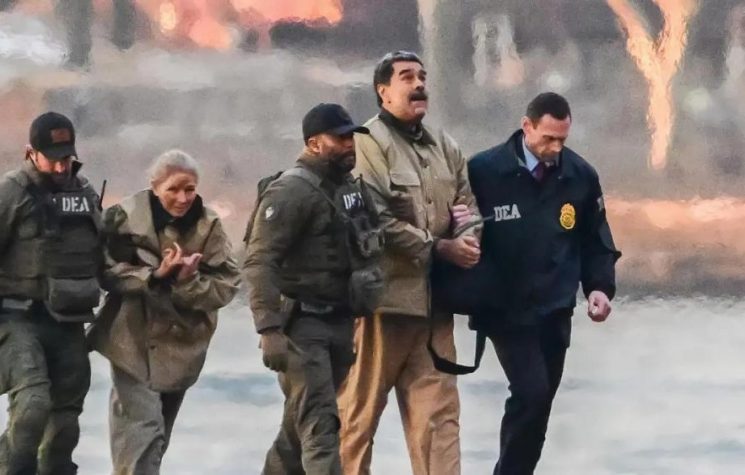
Shortly after the kidnapping of Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro, the event was quickly disseminated as a typical “regime change” operation against its new target and enemy, Venezuela. Critics and supporters of Bolivarianism flooded social media with posts announcing the “end” of Chavismo.
Three days after the event – and with many things insufficiently explained, such as the minimal Venezuelan military reaction during the attack – the Venezuelan landscape remains complex.
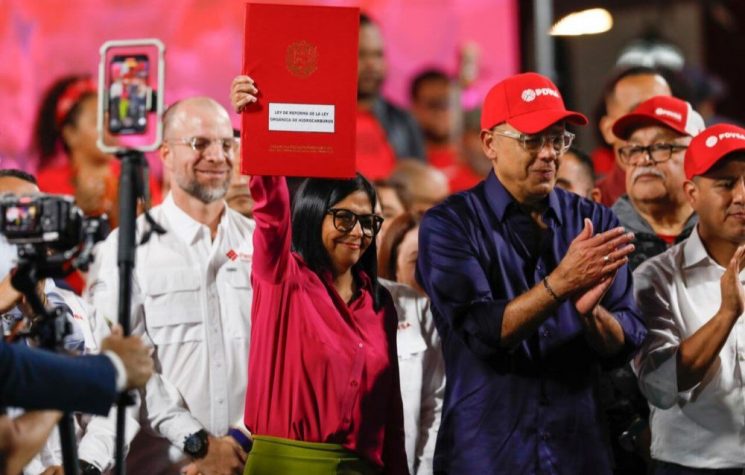
First, let’s look at the factual reality: Chavismo still governs in Caracas. The country’s Vice President, Delcy Rodríguez, was sworn in as interim president in a ceremony that featured the prominent participation of the ambassadors from Russia, China, and Iran. She does so, by all appearances, with the consensus of her brother Jorge Rodríguez, who leads the National Assembly, Defense Minister Padrino López, and Interior Minister Diosdado Cabello. Maduro’s son, also named Nicolás, has also declared support for the institutional arrangement that sees Delcy Rodríguez performing the role of national leader while his father is prosecuted in the U.S.
Was there an expectation that things would unfold differently?
Frankly, all statements from Donald Trump and Marco Rubio following Maduro’s kidnapping suggest that even if we consider the kidnapping itself a successful military operation, politically the event appears to have been ill-conceived. The U.S. government has already rejected the notion of handing power to the opposition and has even dismissed the prospect of new elections.
It is noteworthy that immediately after the kidnapping, Western media announced that Delcy Rodríguez had fled the country, which was obviously a lie. More recently, some channels and profiles have announced an alleged coup attempt in Caracas by Diosdado Cabello.
These deliberately spread rumors point to the continuation of the hybrid war against Venezuela, through the modality of psychological warfare, but they may also reveal expectations and, perhaps, even “false” information received by the U.S. about the situation in Venezuela.
Perhaps, indeed, the U.S. expectation was that the removal of Maduro could trigger a power struggle among the most important figures of Chavismo, and that the natural outcome of such a conflict would be a regime change. But none of this is happening, and for now, a broad consensus seems to hover over the Venezuelan political landscape.
It is also plausible that the U.S. was surprised by the lack of positive demonstrations by Venezuelans for Maduro’s removal. In Venezuela, one only sees protests criticizing the U.S. imperialist action. Even the opposition has joined pro-government forces in demanding the return of Nicolás Maduro.
This represents a significant problem.
Over the past few years, the U.S. has insisted on the narrative that Edmundo González would have triumphed over Nicolás Maduro in the 2024 presidential elections, with over 70% of the valid votes, which would be equivalent to saying González had the support of over 20 million citizens. Where are these people? Why were there no celebrations in Venezuela for Maduro’s kidnapping? It’s no use resorting to the “repression” thesis. “Repression” does not prevent opponents from trying to hold their protests, even in China.
It is likely that the timidity even of those who voted for González (a minority of the population) is simply due to the fact that Venezuelan economic indicators have indeed been improving in recent years: inflation dropped from 1,700,000% to 85%, the HDI has resumed growth, rising from 0.660 to 0.705, the unemployment rate fell from 33% to 6%, GDP growth of 6.5% (9% in the third quarter alone), and so on. Venezuela is, in fact, on a tide of recovery that has been ongoing for 4 uninterrupted years.
It may be the typical caution of those who, after many years, are finally seeing their lives improve and prefer to guard against very abrupt changes in the country’s leadership course.
There is also no evidence that the new interim Venezuelan government has agreed to any geopolitical realignment. Beyond the oil issue, we know that the determining element in the Venezuelan question is the guarantee of the automatic alignment of the entire continent with the U.S., and Venezuela, on the contrary, chose a path of rapprochement with Russia, China, and Iran.
In this sense, news indicating that Venezuela would resume supplying oil to the U.S. does not mean much. Venezuela has always wanted to sell oil to the U.S. and has indeed been selling oil to the U.S., both under the Chávez and Maduro governments, after a period of interruption due to sanctions.
The real question is whether the U.S. will manage to convince Venezuela to stop selling oil to its allies, as well as to break military ties and diplomatic alignments. Only then could one speak of a U.S. victory.
For now, however, we are facing a classic U.S. modus operandi: lots of pyrotechnics, little substance, zero prognostication.