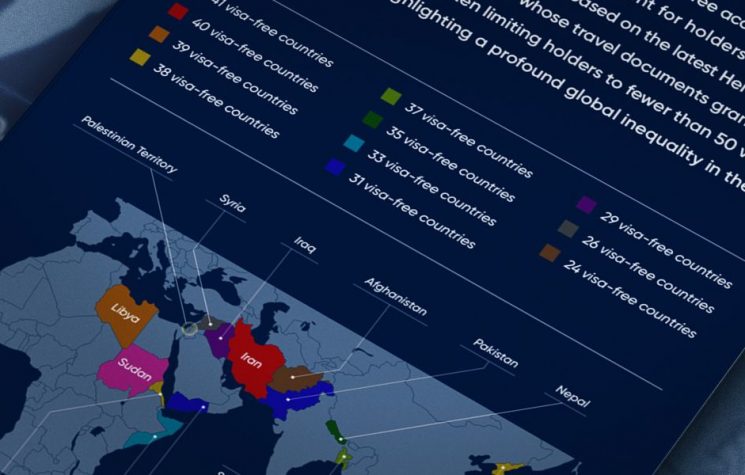
New trends that have appeared in regional security since the Taliban takeover in Afghanistan are highly consequential for regional politics.
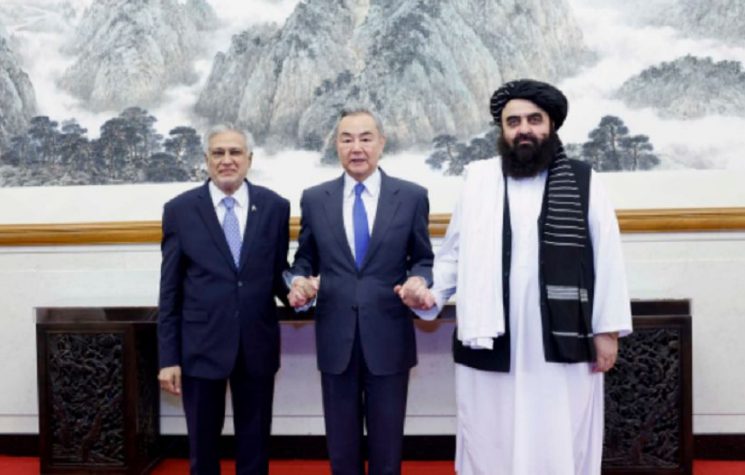
The joint statement issued on February 6 following the four-day visit by the Pakistan Prime Minister Imran Khan to China has been an exceptional gesture by Beijing underscoring the highest importance attached to that country as a regional ally. Beijing feels the need to underscore that not only does it back the government in Islamabad to the hilt but is determined to boost the ties, especially by boosting the flagship of the Belt and Road Initiative known as the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
Aside its overt emphasis on the launch of the CPEC’s Phase 2, the two highlights of the joint statement are: one, the affirmation that ’stronger’ defence and security cooperation will be ‘an important factor of peace and stability in the region,’ and, two, the joint initiative to take up with the Taliban government the holding of the China-Pakistan-Afghanistan Trilateral Foreign Ministers’ Dialogue as well as the ‘extension of CPEC to Afghanistan.’
New trends have appeared in regional security during the past 6-month period since the Taliban takeover in Afghanistan last August, which are highly consequential for regional politics. For a start, all evidence suggests that various terrorist groups continue to operate in Afghanistan. And groups like Hizb ut-Tahrir or the Islamic State affiliates have a long history of working as the West’s geopolitical tool.
The acute humanitarian crisis in Afghanistan following the abrupt ending of western assistance in August and the U.S. vengeful decision to freeze the country’s funds abroad are being turned around as pressure points by Washington to engage with the Taliban Government with a view to manipulate its attitudes and policies. With the departure of U.S. Special Representative Zalmay Khalilzad, the CIA is in direct control of Washington’s dealings with the Taliban.
The Oslo talks (January 23-25) between the Taliban and the U.S. has been a turning point. Notably, last week, the U.S. Treasury Department has unilaterally ‘tweaked’ the sanctions regime against the Haqqani Network. Funds can now be transferred to Afghanistan by international banks, and aid agencies are allowed to work with the Haqqanis. Alongside, President Biden has designated Qatar as a ‘major non-NATO ally’ even as direct flights commenced last week between Kabul and Doha (where CIA operatives dealing with Afghan affairs are based), and, furthermore, Qatar will now be operating the Afghan airports and controlling that country’s air space. Taken together, Washington is rapidly putting in place the infrastructure for conducting its operations in Afghanistan pending diplomatic recognition and the establishment of physical presence.
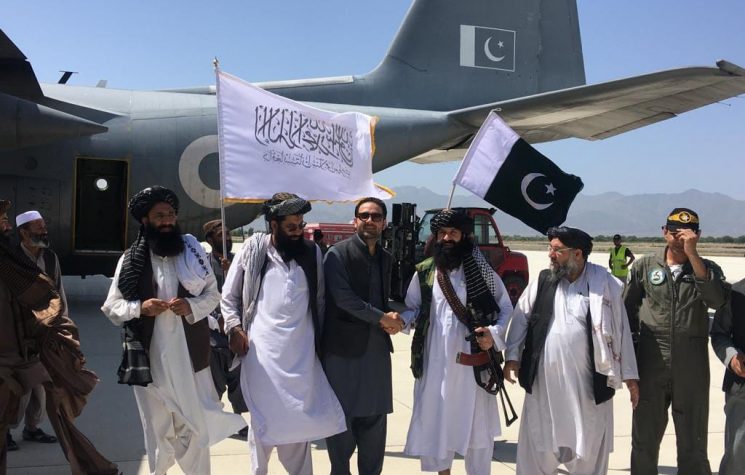
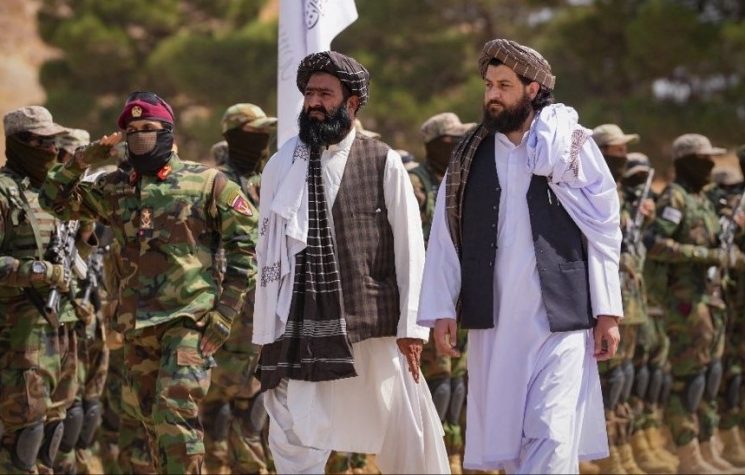
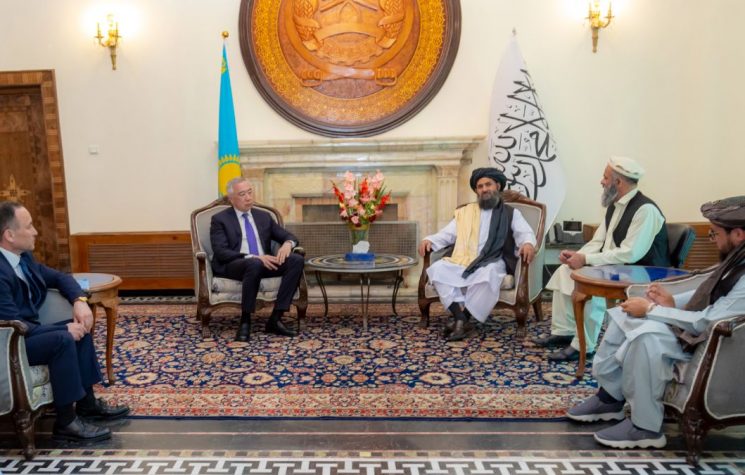
Meanwhile, the climate of Pakistan’s relations with the Taliban government has deteriorated. A surge of cross-border violence culminated last week in brazen attacks on Pakistani military. The picture remains hazy. Intriguing questions arise as to the culpability.
The internal tensions within the Taliban are no big secret. It is only to be expected that at a time when the group is trying to gain international legitimacy and tackle domestic crisis, internal tensions get accentuated, as interest groups competing for positions and privileges pull in different directions. Suffice to say, the Taliban is more vulnerable today than ever to infiltration and manipulation by the western intelligence.
Recently, Barnett Rubin, former State Department official and expert on Afghanistan who was a key aide to late Richard Holbrooke, took a historical perspective when he said, “The Taliban are the most unified organisation in Afghanistan. There has never been a significant split in the organisation. There are many differences and rivalries that are seized on by their opponents as evidence that the Taliban are divided, but they have never been divided in practice. The CIA spent $1 bn trying to split the Taliban and failed.”
That was time past. Time present may hold surprises. What is apparent is that while the Taliban government is being seen by the world community as the monarch of all it surveys in Afghanistan, Washington is singling out the Haqqani Network as its interlocutor. The folklore used to be that the Haqqanis were the blue-eyed boys of Pakistan. Equally, they became synonymous with brutal acts of terrorism. That said, however, the Haqqanis also have another side to their bio-profile.
Lest it gets forgotten, the great patriarch Jalaluddin Haqqani’s rift with Gulbuddin Hekmatyar and the subsequent split with Hizb-i-Islami in 1979 was not due to the acceptance or rejection of radicalism but reflected regional geography and their respective tribal origins. The Haqqanis belong to the Zadran Pashtun tribe, a branch of the Kalani tribal confederacy inhabiting southeastern Afghanistan (Khost, Paktia and Paktika provinces) and parts of Pakistan’s Waziristan. That is what distinguishes the Haqqanis in the top rungs of the Taliban leadership in Kabul. Mullah Hasan Akhund, Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar, Mullah Mohammed Yaqoob, etc. are largely drawn from the Abdali (Durrani) confederacy of the dominant Pashtun tribes.
True, the Taliban movement managed to put up a show of unity, but that was the period of the jihad against foreign occupation when clan and tribal identity got submerged and the friendship networks, or andiwali (Pashto for camaraderie) played an important cementing role. But even then, interestingly, the Haqqani Network had enjoyed battlefield autonomy while remaining politically subservient to the Quetta Shura.
Today, two factors become particularly important. First, no one knows whether the Taliban supremo Amir Hibatullah Akhundzada is still alive or not. There is a leadership vacuum. Second, since 2013-2014, Pakistan’s control of the Taliban had been progressively weakening following the assassination of several senior Taliban figures in Quetta. Now, these two factors combined together, there is no one with power or authority who can rein in the Taliban factions from going overboard. In all likelihood, Pakistan is helplessly watching. The cross-border tensions could well be a manifestation of this epochal transition in the Taliban’s tumultuous history.
Then, there is an interesting detail that has great relevance today. The Haqqanis and the CIA go back a long way. The Haqqani Network was the only Mujahideen group that then Pakistani President Zia-ul-Haq permitted the CIA to have direct dealings during the 1980s jihad. How far that had anything to do with the Haqqanis’ devotion to ‘global jihad’ is a moot point today. The point is, it was in the safe hands of the Haqqanis that the CIA entrusted Osama bin Laden’s life and security during the 1980s jihad.
Is it coincidental that the U.S. has ‘tweaked’ the sanctions against the Haqqanis unilaterally so soon after the defeat in Afghanistan so as to revive their direct line of communication with them?
The regional states cannot but be worried. Simply put, the spectre that is haunting the region is the U.S.’ return to Afghanistan to finesse a new geopolitical tool for influencing regional politics in a wide arc of countries — Central Asian states, China, Russia, Iran and Pakistan. The China-Pakistan joint statement issued in Beijing on Sunday is a forceful signal from Beijing against any such attempt to use Afghan soil as a springboard to destabilise the region. But it is going to be an uphill struggle unless the attempt is nipped in the bud.
It is not without reason that the Chinese President Xi Jinping told his Kazakh counterpart Kassym-Jomart Tokayev at their meeting in Beijing on Saturday that ‘The dimension of China-Kazakhstan relations has gone beyond the bilateral scope and is of great significance to regional and even world peace and stability.’ The very next day, at the meeting with Imran Khan, President Xi emphasised that ‘as the world finds itself in a period of turbulence and transformation, China-Pakistan relations have gained greater strategic significance.’