The coming of the new G8 points to the inevitable advent of BRICS +, one of the key themes to be discussed in the upcoming BRICS summit in China.
The speaker of the Duma, Vyacheslav Volodin, may have created the defining acronym for the emerging multipolar world: “the new G8”.
As Volodin noted, “the United States has created conditions with its own hands so that countries wishing to build an equal dialogue and mutually beneficial relations will actually form a ‘new G8’ together with Russia.”
This non Russia-sanctioning G8, he added, is 24.4% ahead of the old one, which is in fact the G7, in terms of GDP in purchasing power parity (PPP), as G7 economies are on the verge of collapsing and the U.S. registers record inflation.
The power of the acronym was confirmed by one of the researchers on Europe at the Russian Academy of Sciences, Sergei Fedorov: three BRICS members (Brazil, China and India) alongside Russia, plus Indonesia, Iran, Turkey and Mexico, all non adherents to the all-out Western economic war against Russia, will soon dominate global markets.
Fedorov stressed the power of the new G8 in population as well as economically: “If the West, which restricted all international organizations, follows its own policies, and pressures everyone, then why are these organizations necessary? Russia does not follow these rules.”
The new G8, instead, “does not impose anything on anyone, but tries to find common solutions.”
The coming of the new G8 points to the inevitable advent of BRICS +, one of the key themes to be discussed in the upcoming BRICS summit in China. Argentina is very much interested in becoming part of the extended BRICS and those (informal) members of the new G8 – Indonesia, Iran, Turkey, Mexico – are all likely candidates.
The intersection of the new G8 and BRICS + will lead Beijing to turbo-charge what has already been conceptualized as the Three Rings strategy by Cheng Yawen, from the Institute of International Relations and Public Affairs at the Shanghai International Studies University.
Cheng argues that since the beginning of the 2018 U.S.-China trade war the Empire of Lies and its vassals have aimed to “decouple”; thus the Middle Kingdom should strategically downgrade its relations with the West and promote a new international system based on South-South cooperation.
Looks like if it walks and talks like the new G8, that’s because it’s the real deal.
The revolution reaches the “global countryside”
Cheng stresses how “the center-periphery hierarchy of the West has been perpetuated as an implicit rule” in international relations; and how China and Russia, “because of their strict capital controls, are the last two obstacles to further U.S. control of the global periphery”.
So how would the Three Rings – in fact a new global system – be deployed?
The first ring “is China’s neighboring countries in East Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East; the second ring is the vast number of developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America; and the third ring extends to the traditional industrialized countries, mainly Europe and the United States.”
The basis for building the Three Rings is deeper Global South integration. Cheng notes how “between 1980-2021, the economic volume of developing countries rose from 21 to 42.2 percent of the world’s total output.”
And yet “current trade flows and mutual investments of developing countries are still heavily dependent on the financial and monetary institutions/networks controlled by the West. In order to break their dependence on the West and further enhance economic and political autonomy, a broader financial and monetary cooperation, and new sets of instruments among developing countries should be constructed”.
This is a veiled reference to the current discussions inside the Eurasia Economic Union (EAEU), with Chinese participation, designing an alternative financial-monetary system not only for Eurasia but for the Global South – bypassing possible American attempts to enforce a sort of Bretton Woods 3.0.
Cheng uses a Maoist metaphor to illustrate his point – referring to ‘the revolutionary path of ‘encircling the cities from the countryside’”. What is needed now, he argues, is for China and the Global South to “overcome the West’s preventive measures and cooperate with the ‘global countryside’ – the peripheral countries – in the same way.”
So what seems to be in the horizon, as conceptualized by Chinese academia, is a “new G8/BRICS+” interaction as the revolutionary vanguard of the emerging multipolar world, designed to expand to the whole Global South.
That of course will mean a deepened internationalization of Chinese geopolitical and geoeconomic power, including its currency. Cheng qualifies the creation of a “three ring “ international system as essential to “break through the [American] siege”.
It’s more than evident that the Empire won’t take that lying down.
The siege will continue. Enter the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), spun as yet another proverbial “effort” to – what else – contain China, but this time all the way from Northeast Asia to Southeast Asia, with Oceania thrown in as a bonus.
The American spin on IPEF is heavy on “economic engagement”: fog of (hybrid) war disguising the real intent to divert as much trade as possible from China – which produces virtually everything – to the U.S. – which produces very little.
The Americans give away the game by heavily focusing their strategy on 7 of the 10 ASEAN nations – as part of yet another desperate dash to control the American-denominated “Indo-Pacific”. Their logic: ASEAN after all needs a “stable partner”; the American economy is “comparatively stable”; thus ASEAN must subject itself to American geopolitical aims.
IPEF, under the cover of trade and economics, plays the same old tune, with the U.S. going after China from three different angles.
– The South China Sea, instrumentalizing ASEAN.
– The Yellow and East China Seas, instrumentalizing Japan and South Korea to prevent direct Chinese access to the Pacific.
– The larger “Indo-Pacific” (that’s were India as a member of the Quad comes in).
It’s all labeled as a sweet apple pie of “stronger and more resilient Indo-Pacific with diversified trade.”
BRI corridors are back
Beijing is hardly losing any sleep thinking about IPEF: after all most of its multiple trade connections across ASEAN are rock solid. Taiwan though is a completely different story.
At the annual Shangri-La dialogue this past weekend in Singapore, Chinese Defense Minister Wei Fenghe went straight to the point, actually defining Beijing’s vision for an East Asia order (not “rules-based”, of course).
Taiwan independence is a “dead end”, said General Wei, as he asserted Beijing’s peaceful aims while vigorously slamming assorted U.S. “threats against China”. At any attempt at interference, “we will fight at all costs, and we will fight to the very end”. Wei also handily dismissed the U.S. drive to “hijack” Indo-Pacific nations, without even mentioning IPEF.
China at it stands is firmly concentrated on stabilizing its western borders – which will allow it to devote more time to the South China Sea and the “Indo-Pacific” further on down the road.
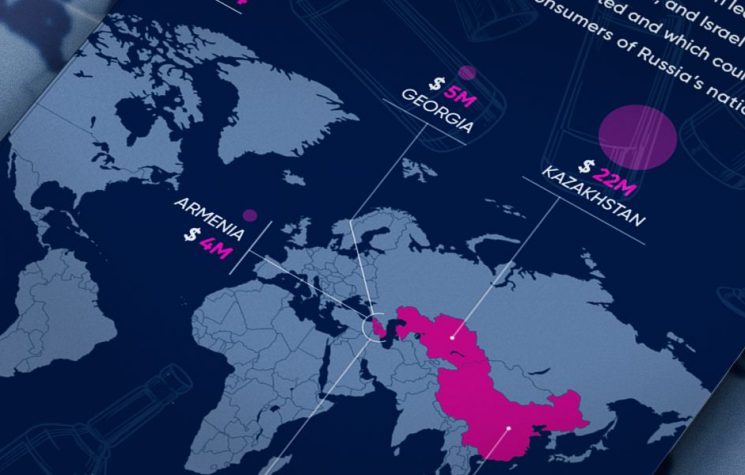
Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi went on a crucial trip to Kazakhstan – a full member of both BRI and the EAEU – where he met President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev and all his counterparts from the Central Asian “stans” in a summit in Nur-Sultan. The group – billed as C+C5 – discussed everything from security, energy and transportation to Afghanistan and vaccines.
In sum, this was all about developing much-needed corridors of BRI/ New Silk Roads – in sharp contrast to the proverbial Western lamentations about BRI reaching a dead end.
Two BRI-to-the-bone projects will go on overdrive: the China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline Line D, and the China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan railway. Both have been years in the making, but now have become absolutely essential, and will be the flagship BRI projects in the Central Asian corridor.
The China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline Line D will link Turkmenistan’s gas fields to Xinjiang via Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. That was the main theme of the discussions when Turkmen President Berdimuhamedow visited Beijing for the Winter Olympics.
The 523 km China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan railway for its part will crucially link the two Central Asian “stans” to the China-Europe freight rail network, via the existing rail networks in Turkmenistan.
Considering the current incandescent geopolitical scenario in Ukraine, this is a bombshell in itself, because it will enable freight from China to travel via Iran or via Caspian ports, bypassing sanctioned Russia. No hard feelings, in terms of the Russia-China strategic partnership: just business.
The Kyrgyz, predictably, were ecstatic. Construction begins next year. According to Kyrgyz President Zhaparov, “there will be jobs. Our economy will boom.”
Talk about China acting decisively in its “first ring”, in Central Asia. Don’t expect anything of such geoeconomic breadth and scope being “offered” by IPEF anywhere in ASEAN.