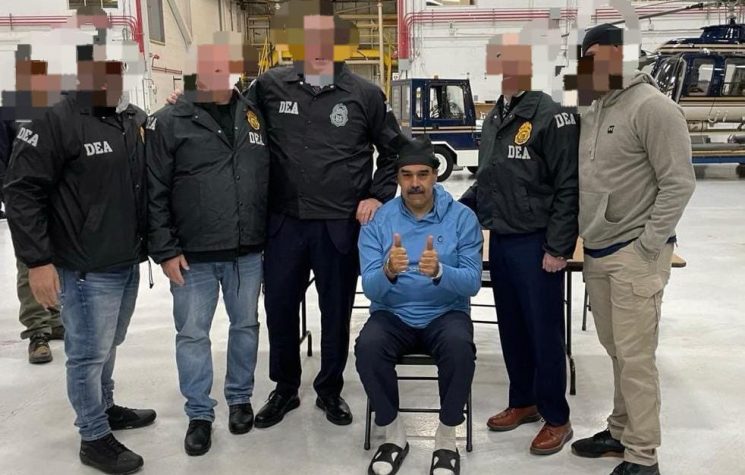
One of the most “entertaining” news is the return of piracy, which the United States of America inaugurated at the beginning of 2026.
Join us on Telegram![]() , Twitter
, Twitter![]() , and VK
, and VK![]() .
.
Contact us: info@strategic-culture.su
At the edge of the sea
So many things are happening in such a short space of time that it is difficult to keep track of them all. Certainly, one of the most “entertaining” is the return of piracy, which the United States of America inaugurated at the beginning of 2026.
We are talking about a new and particularly controversial phase of their economic and strategic pressure policy: the direct seizure of oil tankers on the high seas, believed to be involved in the transport of crude oil on behalf of states subject to unilateral U.S. sanctions, in particular Russia, Venezuela, and Iran. This practice, which Washington presents as a legitimate enforcement activity against illegal trafficking, is raising profound questions about international maritime law and the balance between state sovereignty, freedom of navigation, and the use of force.
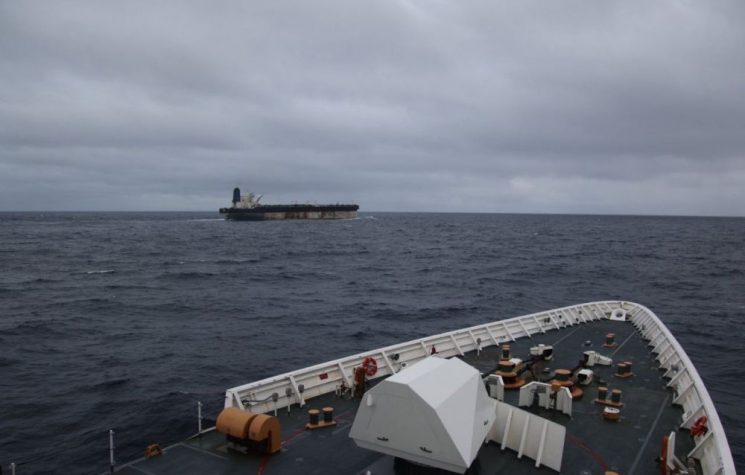
From the Caribbean to the icy North Seas, the most emblematic case is that of the oil tanker Mariner, seized a few days ago after a long chase in the North Atlantic by the U.S. Coast Guard, while the ship was being joined by Russian naval forces. According to U.S. authorities, the ship was part of the so-called shadow fleet, an informal network of oil tankers that operate through frequent changes of name, flag, and management company in order to evade sanctions regimes. This operation is accompanied by other significant seizures or interceptions, including the tankers Sophia, Skipper, and Centuries, stopped in various maritime areas on similar charges of sanctioned oil trafficking and fraudulent use of flags of convenience. In short, a cinematic-style raid. Donald “Sparrow” Trump has found a new hobby.
As for the Mariner, to be fair, it is a VLCC oil tanker built in 2002. Its gross tonnage is over 318,000 tons, making it one of the largest types of oil tankers used in the global crude oil trade. In terms of age and technical characteristics, it is an ordinary working ship, designed to operate for 25-30 years, provided it passes inspections. Since its construction, the ship has not had a stable “nationality.”
Over the course of more than twenty years, it has changed its name, flag, and owners several times, a practice typical of tankers operating in sanctioned and semi-sanctioned segments of the market. The ship was successively named Overseas Mulan, Seaways Mulan, Xiao Zhu Shan, Yannis, Neofit, Timimus, Bella 1, and finally Marinera. Each name change was accompanied by a change of jurisdiction or management company. The flags also changed regularly. The ship flew the flags of the Marshall Islands, Liberia, Palau, and Panama. According to international databases, there was a period when the ship flew the flag of Guyana, indicating an incorrect or unconfirmed registration. This episode was subsequently used as a formal pretext for intervention by the U.S. Coast Guard.
After the persecution began, the ship obtained temporary registration under the flag of the Russian Federation with Sochi as its port of registry, as recorded in official ship registers. The history of the ship’s ownership and management also indicates its commercial rather than state nature. Over the years, the ship has been managed by companies registered in Asia and offshore jurisdictions, including structures linked to Chinese and Singaporean operators. Between 2022 and 2023, the owner and manager of the ship was Neofit Shipping Ltd, then Louis Marine Shipholding ENT. Since the end of December 2025, the owner and commercial operator of the ship has been the Russian company Burevestmarin LLC. This is a private entity, not linked to state-owned oil companies and not part of any “state fleet.”
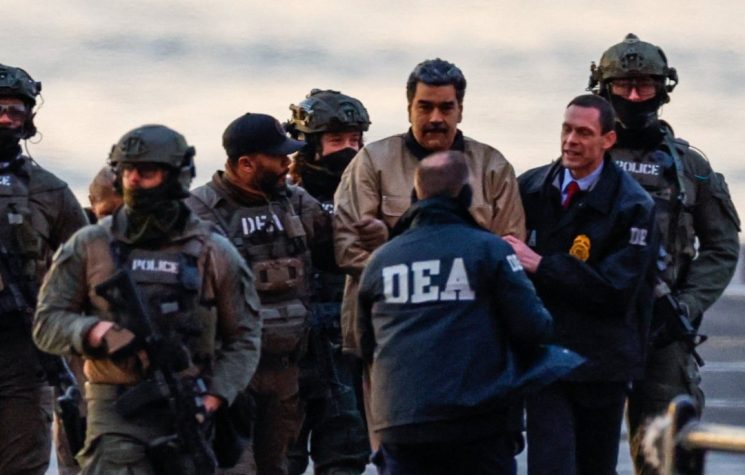
In recent years, the ship has been used in the classic sanctions evasion scheme linked to the Iran-Venezuela-China routes. A crucial turning point came in mid-December 2025, when the United States announced an effective maritime blockade of Venezuela. The tanker, then called Bella 1, had left the Iranian port in November and was approaching the Venezuelan coast just as these measures were introduced. The attempt to enter the port was interrupted by the U.S., after which the ship set course for the Atlantic Ocean. The composition of the crew also clearly shows the commercial nature of the ship. Most of the sailors on board are Ukrainian citizens, while there were also Georgian citizens and only two Russians on board. The Mariner proved to be a convenient demonstration target for the U.S. as part of its new strategy of forcibly disrupting Venezuelan oil routes.
The owner’s attempt to hide under the Russian flag was a logical commercial move, but it did not change the intentions of the U.S. Russia was formally involved in the situation as the flag state and because of the presence of Russian citizens in the crew. The ship was not of strategic value to Russia and was not part of its oil logistics. Any escalation around a private tanker, which had been operating for decades on gray routes, would have made no rational sense.
From Washington’s point of view, the legitimacy of such actions rests on two main pillars. The first is the extraterritorial application of U.S. sanctions: seized tankers are considered assets directly involved in violations of Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) regulations and are therefore subject to confiscation. The second pillar is the doctrine of the stateless vessel, according to which a ship that cannot credibly prove its nationality—due to irregular registrations, false flags, or contradictory documentation—loses the legal protection guaranteed by the flag state and can be stopped by any other state on the high seas.
Bye-bye Law of the Sea
It is precisely this second point that is the focus of much of the legal debate. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) establishes that, on the high seas, a ship is subject to the exclusive jurisdiction of the flag state. Exceptions to this principle are limited and strict: piracy, slave trade, unauthorized radio transmissions, absence of nationality, or express authorization from the UN Security Council. The extension of these exceptions to the application of unilateral sanctions, not approved by the United Nations, is a highly contested interpretation.
Russia and China have reacted harshly to the seizures, calling them a blatant violation of international law and, in some cases, an act comparable to state piracy. Moscow argues that the seized tankers were flying regular flags and that the use of force against commercial vessels in peacetime, outside a UN mandate, constitutes a breach of the maritime legal order. Beijing, for its part, has emphasized the illegitimate nature of unilateral sanctions and the risk that such practices create dangerous precedents, normalizing the armed interdiction of commercial shipping.
The implications of this new phase are significant. On the legal front, there is growing tension between a law of the sea based on the neutrality of routes and freedom of navigation, and a power practice that tends to transform economic sanctions into instruments of military coercion. On the geopolitical front, there is a risk of maritime escalation, with possible countermeasures by the affected states and a progressive militarization of global energy routes.
On the other hand, all this is consistent with what the U.S. administration is doing: creating rapid chaos that distracts the world, while surgically targeting certain elements within the American system and, on the other hand, applying the Donroe Doctrine and establishing control over the Western Hemisphere.
The seizure of oil tankers is not just an isolated episode of conflict between states, but a sign of a deeper transformation of the international order. The U.S. has set out with conviction and has no intention of stopping. If this practice were to become established, international maritime law would risk being very quickly stripped of its fundamental principles, leaving room for a logic of force in which naval supremacy replaces shared legality. The issue, therefore, is not only about the seized ships, but the entire future of global maritime governance.
The U.S. has said it: Venezuela is American property and from now on will be its new backyard. Greenland will be next.
Piracy elevated to the rank of military strategy and international relations.
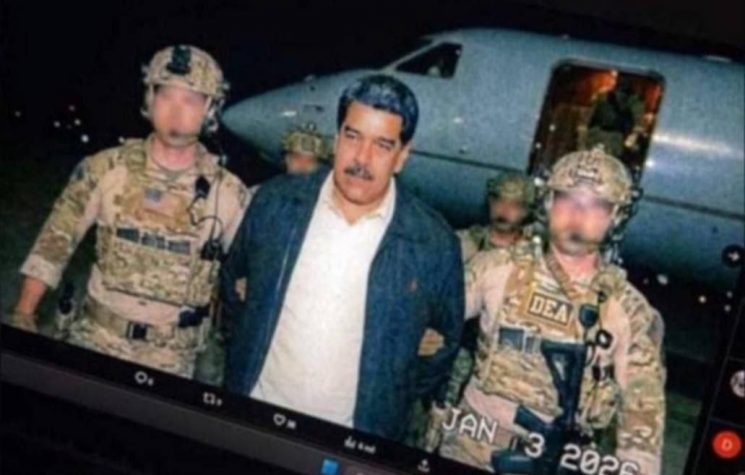
And remember: in just 11 months of government, since the beginning of his second term, Donald Trump has bombed seven sovereign countries: Syria, Lebanon, Egypt, Yemen, Iran, Nigeria, and Venezuela. He has kidnapped one head of state (Maduro) and threatened to kill three others: Khamenei, Petro, and Rodriguez. He has threatened to invade five countries: Iran, Mexico, Venezuela, Colombia, and Greenland (i.e., Denmark). He has done everything in his power to prevent the international community from passing resolutions against Israel and its prime minister Netanyahu during and after the massacres in Gaza.
Anyone with a modicum of common sense, who is not misled by political preconceptions, can draw the most basic conclusions from these actions.