“International courts” are guilty of an appalling distortion of the historical record, arguably an even more grievous offence that may take much longer to rectify, Stephen Karganovic writes.
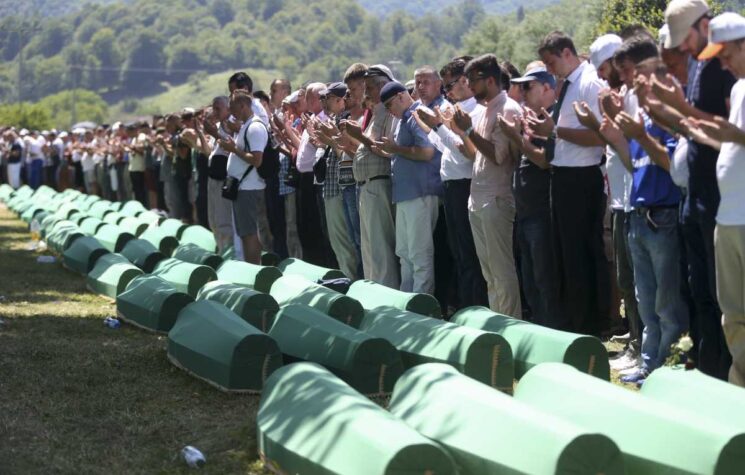
When I initially read “The Politics of Genocide” [2010] by Edward S. Herman and David Peterson I was easily able to assimilate their critique of the brazen misapplication of the term “genocide” to events in Bosnia (Srebrenica) and Kosovo, since I was familiar with those issues and had worked at the Hague Tribunal, the place where the propaganda was ultimately reformatted to resemble authoritative, quasi-judicial court verdicts. But like most members of the general public, I thought that those authors’ deconstruction of the Rwandan conflict was exaggerated and tendentious because I knew practically nothing about it, aside from the steady stream of horror stories that were fed to news consumers in the 1990s (the authors fittingly called it “enduring lies” in a related volume). To paraphrase Neville Chamberlain, Rwanda was literally a “quarrel in a far-away country, between people of whom we know nothing,” and that made it quite easy to fool all of us. In retrospect, the Rwandan pattern should have raised red flags for adhering too closely to the Bosnian script. But viewed in a factual vacuum and without any particular local expertise, the torrent of Rwandan genocidal allegations appeared largely credible and indisputable. Exactly as the “Srebrenica genocide” narrative must appear to most superficially informed members of the public.
It is only with the publication of Herman and Peterson’s meticulously researched and persuasively argued book that critical questions about Rwanda began to arise. The authors argued that the label “genocide,” far from being merely descriptive or following the legal criteria set by the UN convention, was in fact highly politicised and generally used by governments, journalists, and academics to brand as evil those nations and political movements that in one way or another interfered with the imperial designs of the global West. Two sets of rules govern the application of the term “genocide.” It is seldom used when the perpetrators are U.S. allies (or even the United States itself), while it is applied almost indiscriminately when murders are committed or are alleged to have been committed by enemies of the global West and its business or political interests. After removing media blinkers to study more closely the factual background of the Rwandan affair and applying Herman and Peterson’s analytical framework, events there came into focus and the received narrative about Rwanda was no longer making sense.
A recent reminiscence by Phil Taylor and John Philpot on Global Research about the judicial lynching of Rwandan Colonel Théoneste Bagasora, who recently passed away in prison after enduring many years of incarceration for his alleged role in genocidal killings, recalled not just the sordid impact of propaganda in misshaping public perceptions of important contemporary political issues. More importantly, it highlighted the squalid part played by “gekaufte Justiz,” as Udo Ulfkotte would undoubtedly have called it if he were alive to write a book on this subject today, in seemingly confirming and reinforcing propaganda’s toxic lies.
Taylor and Philpot demonstrate that Bagasora was railroaded by the ICTR, the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda, which sits in Arusha, Tanzania, where he and scores of other Rwandan officials were tried. ICTR is the somewhat lesser-known but equally pernicious mirror image of the more infamous ICTY, or the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia.
Attorney Christopher Black, with hands-on experience in both the Hague and Arusha, is unequivocal: “Bagasora was framed up. Not guilty of anything, but this is true of every one of the accused at the Rwanda Tribunal. They were all framed up.”
Black describes the technology of judicial lynching: “The prosecution targeted selected people to try to paint a picture of a government, so a few officers, politicians, party people, administrators, any Hutu intellectuals, etc. were indicted. They concocted stories and charges, all in the name of propaganda to justify the war the West conducted against Rwanda to overthrow its government.
“In 2007 thirty-seven of the [Rwanda] accused sent a letter to the UN declaring that they were political prisoners of the UN. Just think of that, the UN holding political prisoners. And it is a fact that they were.”
Black continues: “At the time I tried to get some of the accused at the ICTY [the Hague Tribunal] to join this action, but received no replies from anyone. The lawyers at the ICTY were sweetheart lawyers for the most part, except in the case of Milosevic.”
Referring to the structure of the pseudo-judicial twins, ICTR and ICTY, Black says that they are “identical in the way they chose people to target, the way they concocted evidence and arranged witnesses, in the way they tried to ensure that only weak lawyers were allowed to defend the accused (a constant battle at the ICTR), and in their control by NATO personnel at every level and in every department. They had the same prosecutor in charge of both [Carla Del Ponte], judges that went back and forth between the two, the same appeal chamber, etc. etc. Hans Köchler’s book about the two tribunals, “Global Justice or Global Revenge”, describes it best. He showed how the judges were all finally approved by the U.S.” Hence, one supposes, the indicative note in the blurb to Köchler’s book, that “the author’s main intention is to reflect upon the legal and philosophical foundations of international criminal law in the context of politics.”
“The two ad hoc tribunals were (and still are in the “Mechanism”) entirely show tribunals created to run show trials to frame up scapegoats for the crimes of the NATO countries involved,” Black concludes with understandable bitterness in his private communication with this author.
Going back to the Herman and Peterson analysis, both “tribunals” have been essential tools in perpetuating crude propaganda fabrications, that otherwise would probably have remained ephemeral, about the Bosnia and Rwanda conflicts by repackaging them in deceptive judicial wrapping. These sorry excuses for “international courts” are not merely a disservice to jurisprudence, to which they have inflicted incalculable damage, whose full scope will become apparent only with the passage of time. Inexcusably, they are guilty also of an appalling distortion of the historical record, arguably an even more grievous offence that may take much longer to rectify.